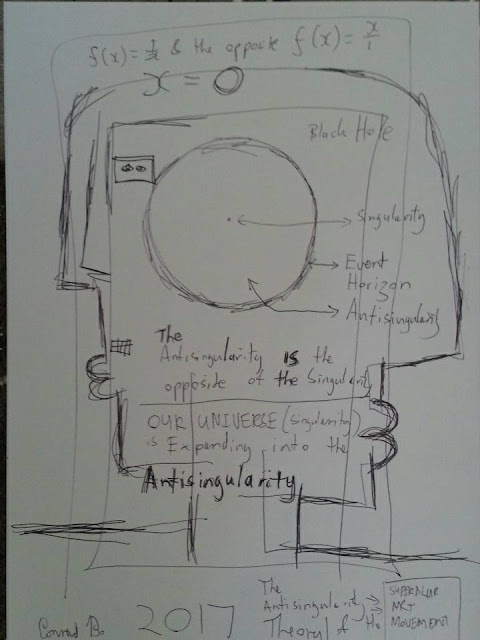
In my attempts to explain the Anti Singularity Theory (Antisingularity) it is important to look at the different mathematics involved.
Black holes are one of the most fascinating objects in the universe, and their mathematical properties have intrigued scientists for decades. A black hole is a region of space where the gravitational pull is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape its grasp. The mathematics of a black hole is complex and involves a combination of general relativity, quantum mechanics, and thermodynamics.
The concept of a black hole was first proposed by John Michell in 1783 and later developed by Pierre-Simon Laplace in 1796. However, it was not until the early 20th century that the mathematical framework for black holes began to take shape. In 1915, Albert Einstein published his theory of general relativity, which revolutionized our understanding of gravity and provided a framework for describing the curvature of spacetime.
One of the key concepts in general relativity is the idea of a singularity, which is a point in spacetime where the gravitational field becomes infinite. In the case of a black hole, the singularity is located at the center of the black hole and is surrounded by an event horizon, which is the boundary beyond which nothing can escape.
The mathematics of a black hole also involves the concept of a metric, which is a mathematical description of the curvature of spacetime. The metric is described by a set of equations known as the Einstein field equations, which relate the curvature of spacetime to the distribution of matter and energy.
One of the most remarkable features of black holes is their ability to distort spacetime. This distortion is caused by the enormous mass of the black hole, which creates a gravitational field so strong that it warps the fabric of spacetime itself. This effect is described by the curvature of spacetime and is most pronounced near the event horizon.
The mathematics of a black hole also involves quantum mechanics, which describes the behavior of particles on a microscopic scale. According to quantum mechanics, particles can exist in multiple states at once, and their behavior is governed by a set of probabilities.
One of the most interesting aspects of black holes from a quantum perspective is the idea of Hawking radiation. According to Stephen Hawking, black holes emit particles over time, which leads to a loss of mass and energy. This process is thought to be caused by quantum effects near the event horizon, where particles can be created and destroyed spontaneously.
Finally, the mathematics of a black hole also involves thermodynamics, which describes the behavior of systems at a macroscopic scale. According to thermodynamics, every system has a certain amount of entropy, which measures the amount of disorder in the system.
In the case of a black hole, the entropy is thought to be proportional to the surface area of the event horizon. This relationship is known as the Bekenstein-Hawking formula and is a key result in the study of black hole thermodynamics.
In conclusion, the mathematics of a black hole is a complex and fascinating subject that involves a combination of general relativity, quantum mechanics, and thermodynamics. The study of black holes has led to many important insights into the nature of gravity, spacetime, and the behavior of particles on a microscopic scale. Despite the many mysteries that still surround black holes, their mathematical properties continue to intrigue scientists and inspire new avenues of research.
Thank you very much for reading this information regarding the Anti Singularity Theory. It is important for me to get as much information out there in this facinating way to look at the Universe.
Regards
Conrad Bo Superblur
Inventor of the Anti Singularity Theory
 |
| Anti Singularity Theory by Conrad Bo Superblur |
 |
| Anti Singularity Theory by Conrad Bo Superblur |
 |
| Anti Singularity Theory by Conrad Bo Superblur |




Comments
Post a Comment