The Anti Singularity (Antisingularity) Theory, Equations Mathematics in Science
In the Anti Singularity (Antisingularity) Theory I describe the area between the Singularity and the Event Horizon of a Black Hole as the Anti Singularity. For this to make sense I have to make use of the available Equations that is available to us.
Equations are mathematical expressions that relate two or more quantities or variables. There are many different types of equations used in various fields of mathematics and science. Here are a few examples:
The quadratic equation: This is a second-degree polynomial equation in one variable, commonly written in the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants and x is the variable.
Newton's second law of motion: This is a fundamental equation in classical mechanics that relates the force applied to an object, its mass, and its acceleration. It is commonly written as F = ma, where F is the force, m is the mass, and a is the acceleration.
The Pythagorean theorem: This is a fundamental theorem in geometry that relates the sides of a right triangle. It states that the square of the hypotenuse (the longest side) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. It can be written as a^2 + b^2 = c^2, where a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
The law of conservation of energy: This is a fundamental principle in physics that states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. It is commonly written as E = mc^2, where E is the energy, m is the mass, and c is the speed of light.
The logistic equation: This is a differential equation commonly used in population dynamics to model the growth of populations. It is written as dN/dt = rN(1 - N/K), where N is the population size, t is time, r is the growth rate, and K is the carrying capacity of the environment.
The Navier-Stokes equation: This is a set of partial differential equations used in fluid mechanics to describe the motion of fluids. It is written as ∂u/∂t + (u · ∇)u = -∇p/ρ + ν∇^2u, where u is the velocity, p is the pressure, ρ is the density, ν is the kinematic viscosity, and ∇ is the gradient operator.
These are just a few examples of the many different types of equations used in mathematics and science.
Thanks a lot for reading this piece relating to the explanation of the Anti Singularity Theory. I have also included some photographs.
Regards
Conrad Bo Superblur
Inventor of the Anti Singularity (Antisingularity) Theory
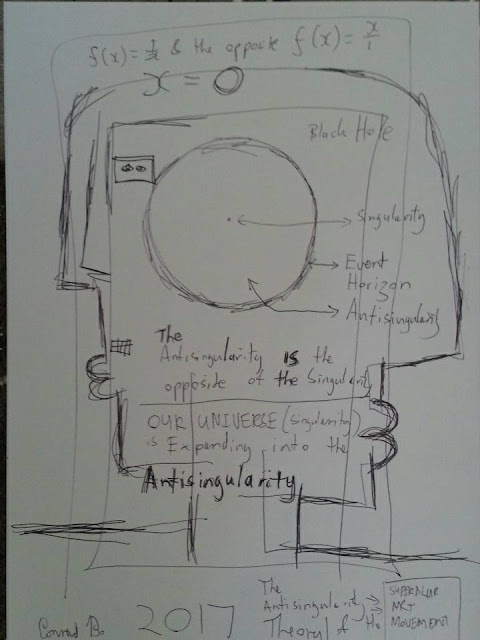 |
| The Anti Singularity (Antisingularity) Theory by Conrad Bo Superblur |
 |
| The Anti Singularity (Antisingularity) Theory by Conrad Bo Superblur |
 |
| The Anti Singularity (Antisingularity) Theory by Conrad Bo Superblur |
 |
| The Anti Singularity (Antisingularity) Theory by Conrad Bo Superblur |
 |
| The Anti Singularity (Antisingularity) Theory by Conrad Bo Superblur |
 |
| The Anti Singularity (Antisingularity) Theory by Conrad Bo Superblur |

Comments
Post a Comment