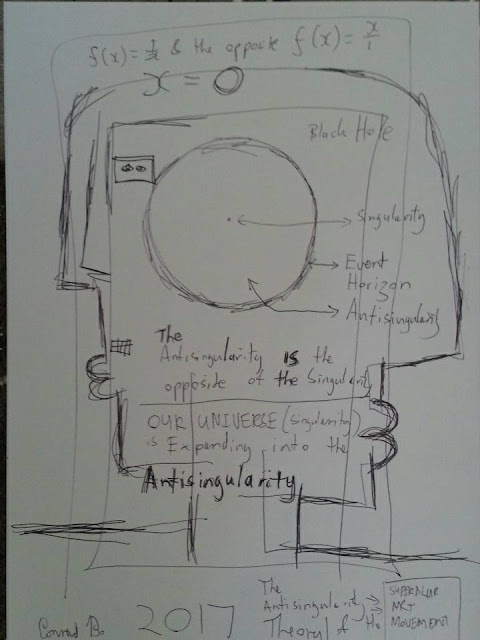
The Anti Singularity Theory (Antisingularity) and Black Holes

I try to explain the Anti Singularity Theory, it is important to look at our current understanding of Black Holes. In the Anti Singularity theory I propose that the space between a Singularity of a Black Hole and the Event Horizon is called the Anti Singularity (Antisingularity). In the Anti Singularity (Antisingularity) the density is zero and the volume is infinite (compared the the Singularity). The Universe consists of 3 things, Singularities, expanding Singularities and the Anti Singularity (Antisingularity). Black holes are one of the most intriguing and fascinating objects in the universe. They are characterized by their immense gravitational pull, which is so strong that even light cannot escape from it. In this paper, we will describe a black hole in terms of mathematics and equations. Mathematical Description: A black hole is described by the Schwarzschild metric, which is a solution to the Einstein field equations of general relativity. The metric is given by: ds^2 ...